Nội dung
For businesses, Cloud Server is the optimal solution to replace traditional forms of storage servers, to increase availability, data security and optimize usage costs.
However, when it comes to Cloud Server, we will need to consider between two important models: Public Cloud (regular cloud services) and Private Cloud (more advanced) to optimize the best usability.
In this article, AZDIGI will help you analyze and learn more about these two concepts.
1. Introduction to Public Cloud and Private Cloud

1.1 Overview of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is a technology model that allows access and use of computer resources such as storage, processing, and software over the network instead of having to invest in physical infrastructure. Instead of managing and maintaining bulky hardware systems on-site, businesses can rent and use these services from cloud providers at reasonable costs and flexible scalability .
In today’s business environment, Cloud Computing plays a vital role in improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and increasing agility as businesses scale. It also helps businesses adapt to rapid market changes, while providing a solid foundation for digital initiatives such as data analytics, artificial intelligence, and remote work.
See more : Cloud Server and applications in business
And in Cloud Computing in general, there are two types of cloud services that are quite popular today: Public Cloud and Private Cloud.
1.2 Overview of Public Cloud and Private Cloud
Public Cloud and Private Cloud are two popular cloud types when classifying cloud servers, each serving different purposes and needs of businesses.
Public Cloud : is a cloud computing service provided by cloud server service providers such as: Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, AZDIGI,… In this model, resources such as servers, storage, and networks are shared among many users, helping to save costs. Public Cloud is suitable for small and medium-sized businesses, or organizations that need to deploy quickly without requiring a high level of security. Users can access services over the internet and only pay for the resources they use.
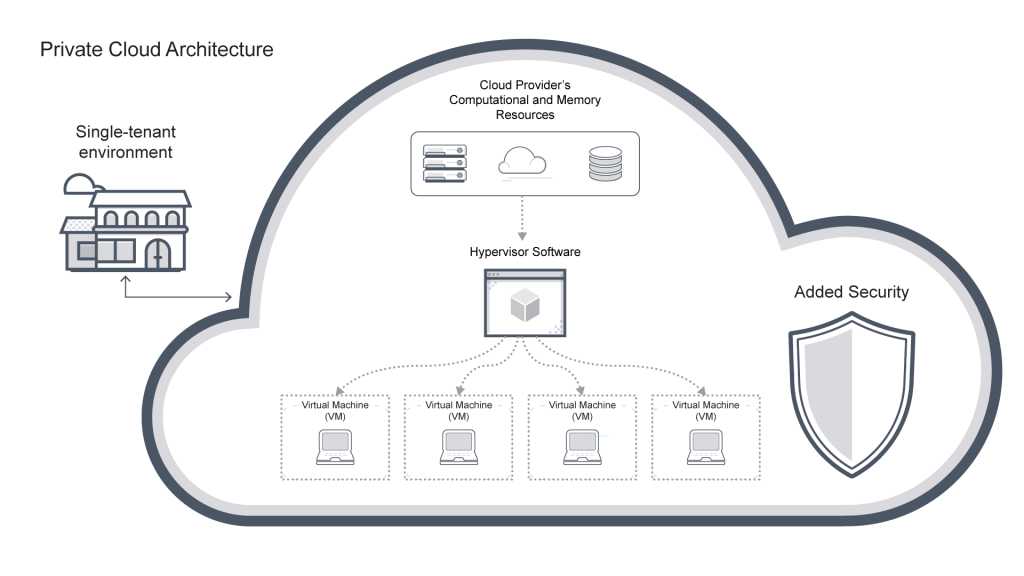
Private Cloud : is a cloud computing environment designed specifically for a single organization or business. In this model, all cloud resources will not be shared with any other users, helping to increase security and control. Private Cloud is usually deployed in the organization’s data center or through a third-party service provider but is still under the control of the business. This type is suitable for large organizations, industries with high security requirements such as finance, healthcare, or businesses that need to customize the infrastructure according to specific needs.
2. Definition and Mechanism of Action
2.1. Public Cloud

Definition: Public Cloud is a cloud computing model in which resources such as servers, storage, and networks are shared among many different users. These resources are provided and managed by cloud service providers such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. Users can access these services over the internet and only pay for what they use, reducing costs and increasing scalability. The Public Cloud model offers flexibility and convenience, suitable for businesses that want to deploy services quickly without investing in their own hardware infrastructure.
How it works: Public Cloud works on a resource sharing mechanism, where servers, storage and networks are provided and managed by cloud service providers. Resources are shared among multiple users through virtualization technology, with virtualized servers operating on the same physical infrastructure. Users access resources over the internet and only pay for what they use, helping to optimize costs. The service provider is responsible for security and infrastructure management, while users can automatically scale up or down resources as needed.
2.2. Private Cloud

Definition: Private Cloud is a cloud computing system designed specifically for a specific organization or business. In this model, all resources such as servers, storage, and networks are not shared with any other users, ensuring high security and control. Private Cloud can be deployed on-premises in the organization’s data center or through a service provider, but the organization has full control and customization of the infrastructure. This allows businesses to optimize and configure the system according to their specific needs, while meeting strict security and legal compliance standards.
How it works: Private Cloud works by providing dedicated server, storage, and networking resources to an organization, not shared with any other users. The system can be managed internally by the organization’s IT team or by a third-party service provider, but the organization still has complete control. This allows businesses to customize the entire infrastructure, from hardware configuration to security and data management, to meet specific needs and high security requirements.
3. Compare the differences between Public Cloud and Private Cloud
3.1. Quyền kiểm soát và quản lý
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud | |
| Control | Users have less control over the infrastructure and hardware because the resources are shared with many other customers. | Users have complete control over the entire infrastructure, as resources are dedicated to a single organization. |
| Manage | The cloud service provider manages the entire infrastructure, including security, maintenance, and upgrades. | Users can directly manage and customize the infrastructure, or hire a third party to manage it. |
Public Cloud is suitable for organizations that need flexibility, cost savings, and do not need to control the entire infrastructure, while Private Cloud is suitable for organizations that need more granular control, higher customization capabilities, and stricter security and policy compliance requirements.
3.2. Security
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud | |
| Security | The provider invests heavily in strong security measures to protect the data of multiple customers, but since resources are shared among multiple users, some security risks may arise. | Greater security because resources are dedicated to one organization, reducing external risks and making it easier to implement specific security policies. |
| Manage | Users do not directly control the security infrastructure, they can only manage security at the application and data level. | Organizations have complete control over security measures, from system configuration to security policies. |
3.3. Chi phí
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud | |
| Expense | – Low cost because there is no need to invest in infrastructure and only pay for the resources used, costs are paid according to usage needs. – Suitable for small and medium enterprises. | – Higher cost due to investment in hardware and software, along with maintenance and management costs. – Suitable for large organizations and businesses. |
3.4. Tính linh hoạt và khả năng mở rộng
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud | |
| Flexibility | Highly scalable, resources can be easily expanded or contracted instantly to meet changing needs without additional investment in hardware. | Good but quite more complex, the ability to customize and scale resources depends on the physical resources of the organization, resulting in additional time and cost. |
| Scalability | Very powerful. Service providers will offer virtually unlimited scalability, suitable for applications and businesses with large and rapidly changing needs. | More limited, scaling requires purchasing and deploying new hardware, which can be time-consuming and costly, depending on the scalability of the current infrastructure. |
3.5. Hiệu suất
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud | |
| Efficiency | – Performance can be very high, but depends on the configuration of the service you choose and how much resources are shared with other customers. – Resources can be easily scaled as needed, improving performance when needed. | – Performance is more stable and less affected by other users because resources are not shared. – Performance may depend on the hardware and software capabilities that the business deploys, as well as how the system is configured. |
3.6. Tài nguyên
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud | |
| Resources | – Provides abundant and scalable resources with flexible costs according to usage. – Ideal for businesses that need large-scale resources but do not want to manage infrastructure. | – Provides dedicated resources to just one organization, with more limited scalability due to hardware and management investment requirements. – Ideal for businesses that need greater control over resources and security. |
3.7. Tính tiêu chuẩn hóa
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud | |
| Standardization | Providing a high level of standardization makes it easy for businesses to integrate and use services, while reducing development and maintenance costs. | Having a lower level of standardization allows businesses to optimize and tailor systems and processes to suit specific requirements. |
4. Specific Use Cases of Public Cloud and Private Cloud
4.1. Khi nào nên sử dụng Public Cloud?
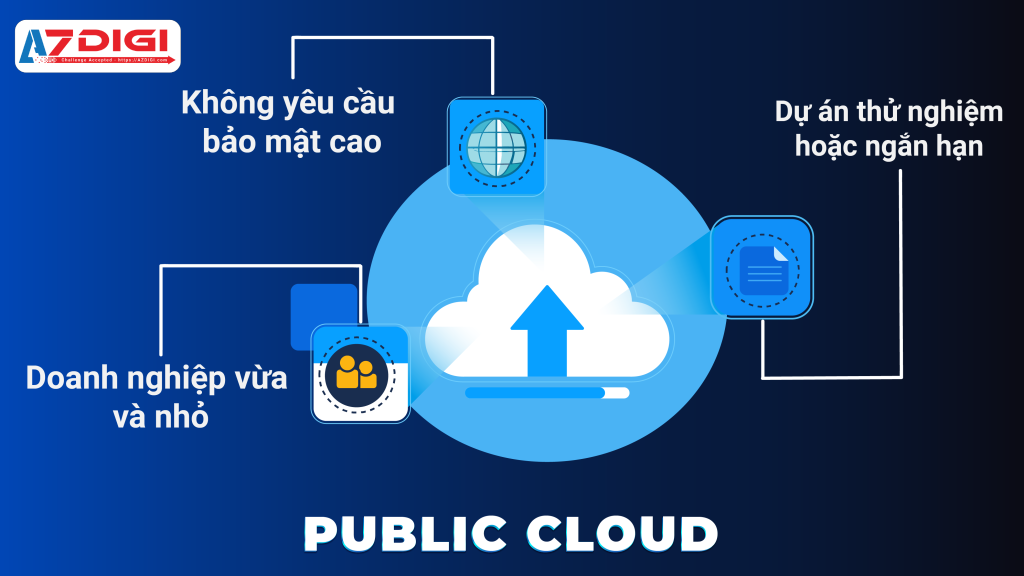
Small and medium enterprises
Public Cloud helps save costs because when using it, businesses only pay for the resources used without having to invest in hardware or infrastructure. Public Cloud provides a flexible and easy-to-deploy solution, suitable for the limited budget of small and medium-sized businesses.
Applications that do not require high security
Public Cloud is a good choice for applications that do not require extremely stringent security levels, such as websites, mobile apps, or SaaS services. Public Cloud providers typically provide basic security and standard features that are sufficient to protect data for these types of applications.
Pilot or short term project
Public Cloud enables quick and easy deployment without long-term infrastructure investment. This is ideal for pilot projects, new product development, or short-term projects, as you can leverage resources on demand and only pay for the time used.
4.2. Khi nào nên sử dụng Private Cloud?
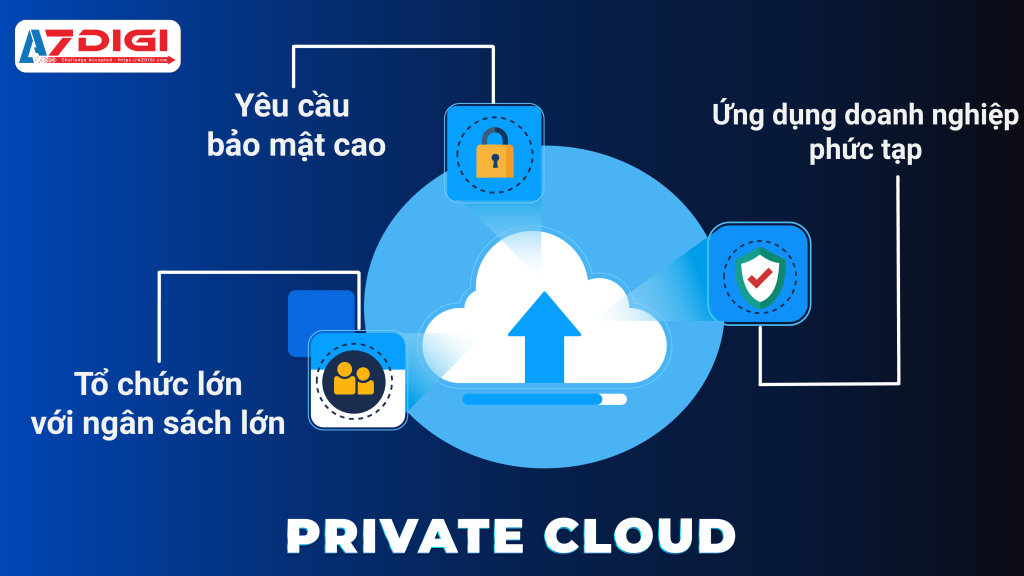
High security requirements
Private Cloud is a good choice for industries such as finance, healthcare, or government organizations because it offers enhanced security and tight controls. Resources are reserved for the organization only, helping to ensure that sensitive data is not shared and security is fully managed by the organization.
Complex business applications
Private Cloud is suitable for ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems or complex enterprise applications because it allows for detailed configuration and control. Enterprises can optimize infrastructure and software to meet the application’s unique technical and process requirements.
Large organization with large budget
Private Cloud is a good choice for large organizations that can afford to invest in their own infrastructure. It allows for deep customization to suit the specific needs of the organization/business, providing flexibility and complete control over the entire system.
5. Advantages and disadvantages of Public Cloud and Private Cloud
Both Public Cloud and Private Cloud have their own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the usage needs, business scale, and security requirements. Understanding the difference between Public Cloud and Private Cloud will help businesses make the right decision, optimize costs and operational efficiency.
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud | |
| Advantage | Low cost : Public Cloud often has lower costs because resources are shared among many users. Businesses only need to pay for the resources they use, helping to optimize costs. Flexible scalability : Easily expand or shrink resources according to demand, suitable for businesses with frequently changing resource requirements. Fast deployment : Services on Public Cloud can be deployed immediately, helping businesses save time when deploying new projects. No need to manage infrastructure : Service providers are responsible for managing, maintaining and updating the infrastructure, helping businesses focus on core business activities without having to worry about IT management. | Complete control : Enterprises have complete control over the infrastructure, including configuration, security, and resource management, allowing them to customize the system to their specific needs. High security : Since resources are not shared with other users, Private Cloud offers a higher level of security, which is especially important for businesses that handle sensitive data. Easier regulatory compliance : Private Cloud makes it easier for businesses to meet security and legal compliance standards, especially in industries that require high levels of security and data management. Consistent performance : Since resources are not shared with other organizations, Private Cloud performance is often more consistent, making it suitable for mission-critical applications and services. |
| Disadvantages | Limited control : Enterprises have little direct control over infrastructure and security, and must rely on the service provider. Security and privacy : While Public Cloud providers implement strong security measures, sharing resources with other customers can increase security and privacy risks. Regulatory compliance : Meeting legal requirements and security standards can be more difficult, especially for industries with high security and compliance requirements, such as finance or healthcare. | High Cost : Private Cloud requires large investments in hardware, software and management infrastructure, making the cost of deployment and maintenance higher than Public Cloud. Limited scalability : Scaling infrastructure in Private Cloud can be complex and expensive, as it depends on the physical resources owned by the business. Complex management : Businesses must manage themselves or hire an IT team to maintain, update and secure the system, which requires high resources and expertise. |
This shows that Public Cloud is suitable for businesses that want to save costs, need to deploy quickly and have flexible needs in expanding resources, but do not require a high level of security and control. Private Cloud is suitable for large businesses, industries that require strict security, and organizations that need comprehensive control over their infrastructure and data, although it comes with higher costs and more complex management.
6. Virtual server rental brand – Cloud Server with optimal quality
AZDIGI is a leading virtual server rental brand – Cloud Server in Vietnam, outstanding with high quality server solutions and outstanding performance. With the goal of bringing businesses and individuals advanced Cloud Server services, AZDIGI is committed to providing server systems with modern technology, using powerful processors such as Intel Xeon Platinum Gen 2 and AMD EPYC Gen 3.
With an optimized infrastructure and an experienced technical team, AZDIGI not only ensures fast data access speed thanks to the use of NVMe hard drives, but also provides flexible services, from Public Cloud to Private Cloud, suitable for all needs from small and medium-sized businesses to large organizations requiring high security. In particular, AZDIGI focuses on customer experience with an easy-to-use control panel, 24/7/365 technical support, and free services such as weekly backups and data transfers.
7. Conclusion
Choosing between Public Cloud and Private Cloud depends on the specific needs and business goals of each enterprise. Public Cloud offers superior convenience and scalability, while Private Cloud ensures a high level of security and tighter control. There is no completely superior solution, instead, enterprises need to carefully consider flexibility, cost, and security requirements to choose the most suitable solution. Understanding the characteristics of each model will help enterprises optimize the effectiveness of cloud technology, thereby improving competitiveness and sustainable development in a volatile business environment.

