Nội dung
Creating a sudo user and disabling SSH access with the root user with 5 simple steps.
Introduction
On Linux, the sudo command is used to allow the user to run the program with the highest privileges, being able to execute all other users’ rights, and with this privilege, we will often see the root user.
In this article, AZDIGI will show you how to create a new user and grant sudo privileges to that user on a Linux server (specifically CentOS 7). And after creating this new user, you can directly use it and perform command line administration without having to log in to the root user as usual.
Implementation Guide
Step 1: SSH into your Linux server
To create a new user and grant sudo privileges on Linux, we first need to SSH or access your VPS/server as root. If you don’t know how to SSH into your VPS/Server, you can refer to the following tutorial:
After successfully SSH, we continue with step 2 to continue the configuration.
Step 2: Create a new user and password
- You can use the command below to add a new User to the system.
For example, I will add a new user named: new_user, then the command structure is as follows: (Remember to replacenew_userwith the new user you need to create).
adduser new_user
- After adding the user, use the command below to set the password for that user with the following command structure:
passwd new_user
Next, you set a new password, you will receive the message that all authentication tokens updated successfully is successful.

Step 3: Grant permissions to the user
- To grant permissions to a new user, use usermod to add a user to the wheel group with the command:
usermod -aG wheel new_user
By default, the server will have a group named wheel, members added to this wheel group will have sudo privileges.
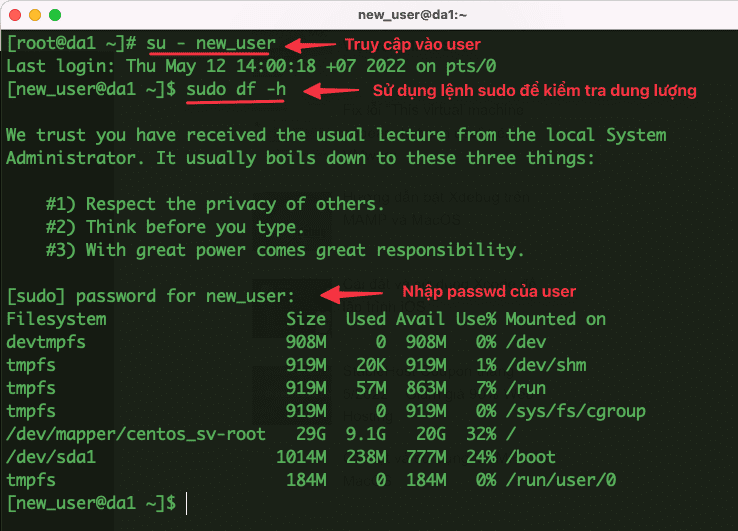
- Check if the user can use the sudo command
To check, you can type the command sudo t.
su - new_user
sudo df -h
If the system displays the results as shown below, it is successful.
Step 4: Disable SSH access with the root user
After creating a new user and granting sudo permissions, if you just want to SSH through the newly created user and want to disable SSH access with the root user, you can do the following:
You open and edit the SSH configuration file according to the path:
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Here, you find the PermitRootLogin line and change it to no.
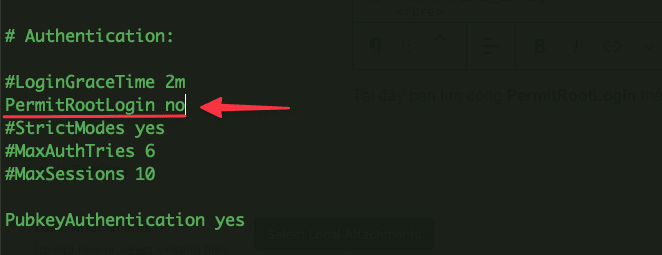
Now you proceed to save the file and restart the sshd service with the command below:
systemctl restart ssh
Step 5: Check the result
Now we will go to check the result after configuration. Below is the result when I SSH back into the server with both the new and root users.
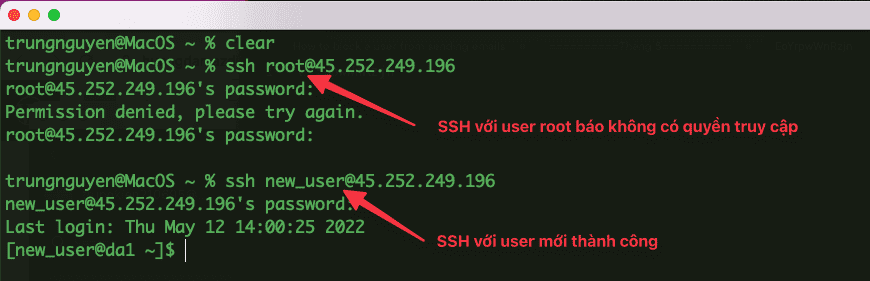
So in this article, AZDIGI showed you how to create and add sudo privileges to a new user to replace the root user, which helps you manage multiple users and make your Linux server more secure. Hope this article is helpful to you, wish you success!
You can refer to other instructions at the link below:
If you need support, you can contact support in the ways below:
- Hotline 247: 028 888 24768 (Ext 0)
- Ticket/Email: You use the email to register for the service and send it directly to: support@azdigi.com .

