Nội dung
How to use RPM on Linux for newbies.
I. Introduction
RPM (Red Hat Package Manager) is an open-source utility used to manage packages on Red Hat systems (RHEL, CentOS, Fedora). An RPM package is a file that contains executable programs, scripts, documents, and some other necessary files. The RPM tool allows users to install, update, uninstall, query, verify and manage rpm packages on Unix/Linux operating systems.
The RPM, formerly known as the .rpm file, includes the compiled software programs and the necessary libraries for these packages and utilities that only work with packages built on the .rpm format. With packages installed from other sources, rpm will not manage.
1.1 Structure of an RPM package
- - . .rpm
For example, telnet-0.17-65.el7_8.x86_64.rpm
- telnet: Package name
- 0.17: Package Version
- 65.el7_8: Package release
- x86_64: Package architecture
- .rpm: Package type
1.2 Modes of the RPM command
- Install: This command is used to install any RPM packages
- Remove: This command is used to remove, remove or uninstall any RPM packages.
- Upgrade: This command to update an existing RPM package
- Verify: This command is used to verify the RPM package
- Query: This command is used to query any RPM package
1.3 Some websites where you can find and download famous RPM packages
II. Guide to using RPM on Linux
Here are some examples of using rpm packages on Linux. Note you must use root privileges to install.
1. Check RPM package
Before installing, you need to check the package under PGP to ensure its safety and origin. Using the –checksig command to check. In the example below, I check the package telnet-0.17-65.el7_8.x86_64.rpm
[root@monitor rpm]# rpm --checksig telnet-0.17-65.el7_8.x86_64.rpm
telnet-0.17-65.el7_8.x86_64.rpm: rsa sha1 (md5) pgp md5 OK
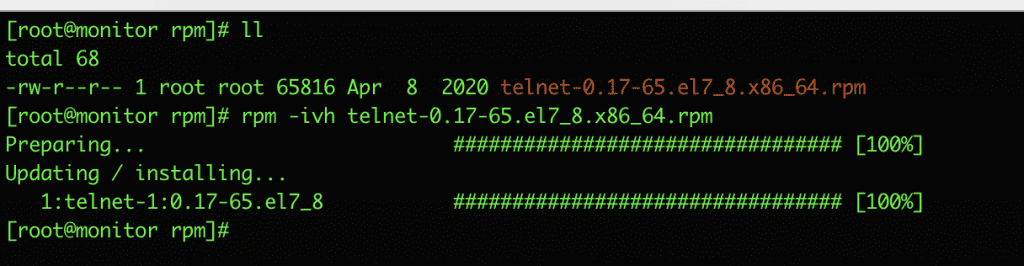
2. Install RPM package
To install an rpm package, add the -i option. I will install a package called telnet-0.17-65.el7_8.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh telnet-0.17-65.el7_8.x86_64.rpm
In there:
- -i : Install a package
- -v : verbose look better
- -h: show
#sign when extracting
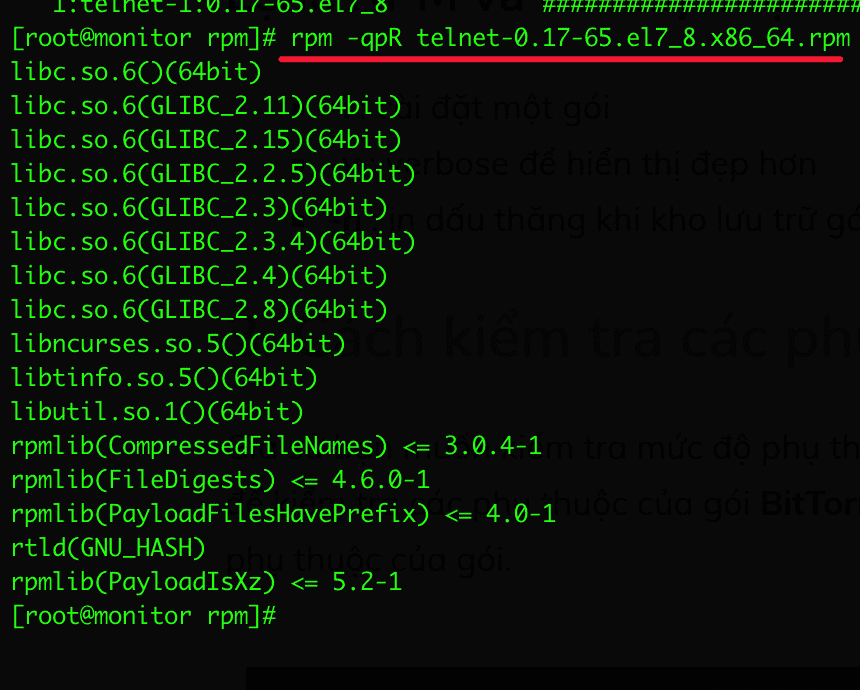
3. Check the dependencies before installing the RPM package
Assuming you want to check the rpm package’s extras before installing or upgrading, use the following command to display the list of subcomponents.
For example, I will check the package telnet-0.17-65.el7_8.x86_64.rpm:
In there:
- -q: Package query
- -p: List the extras this package provides
- -R: List the components on which this package depends
4. Install the RPM package without dependencies
To install RPM packages and ignore dependencies, you use the command and add the following option –nodeps
For example:
rpm -ivh --nodeps telnet-0.17-65.el7_8.x86_64.rpm
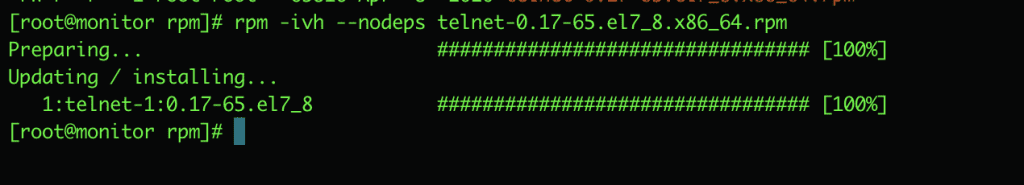
The above command forces the rpm package to be installed by ignoring dependency errors, but if those dependencies are missing, the program won’t work until you reinstall them.
5. Check the installed RPM package
To check the installed package, you use the -q command with the package name.
For example, I’m looking for a package called telnet
rpm -q telnet
Output
telnet-0.17-65.el7_8.x86_64
[root@monitor rpm]#
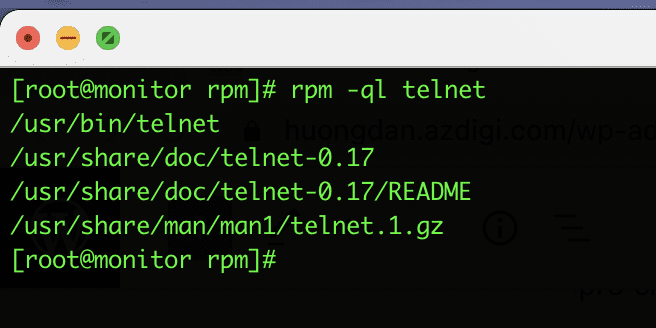
6. List all files of installed RPM packages
To view all the files installed in the rpm package, use the rpm command and the -ql (query list) option.
rpm -ql telnet
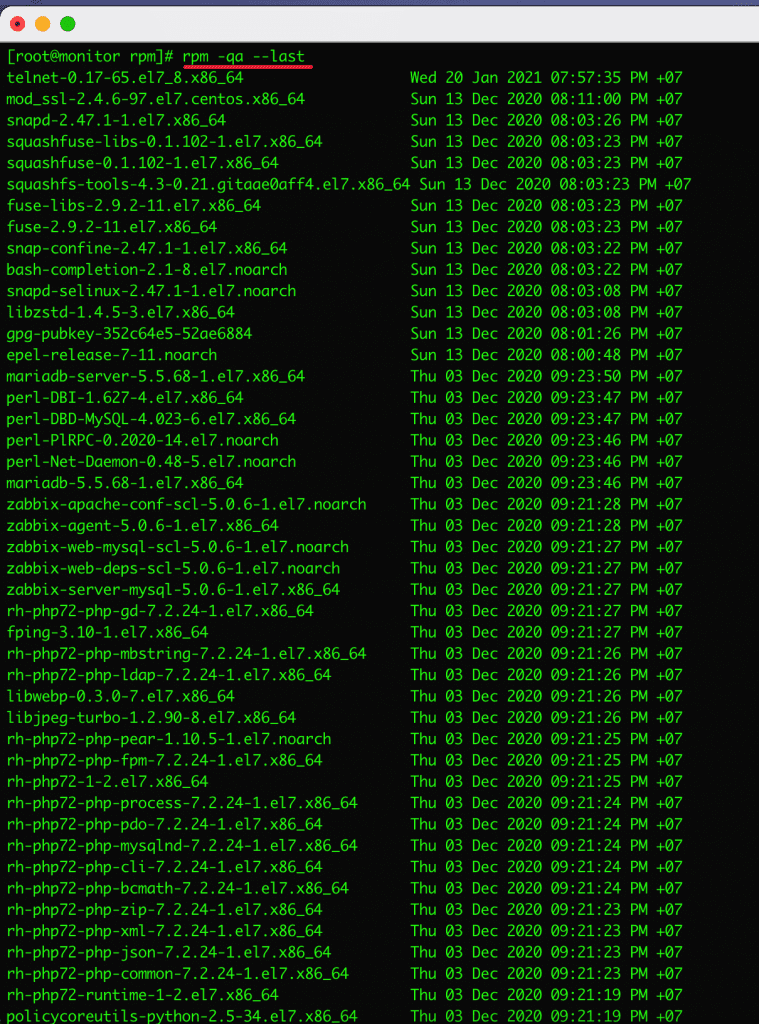
7. List recently installed RPM packages
To list all recently installed rpm packages, use the rpm command with the 2 options -qa --last
rpm -qa --last
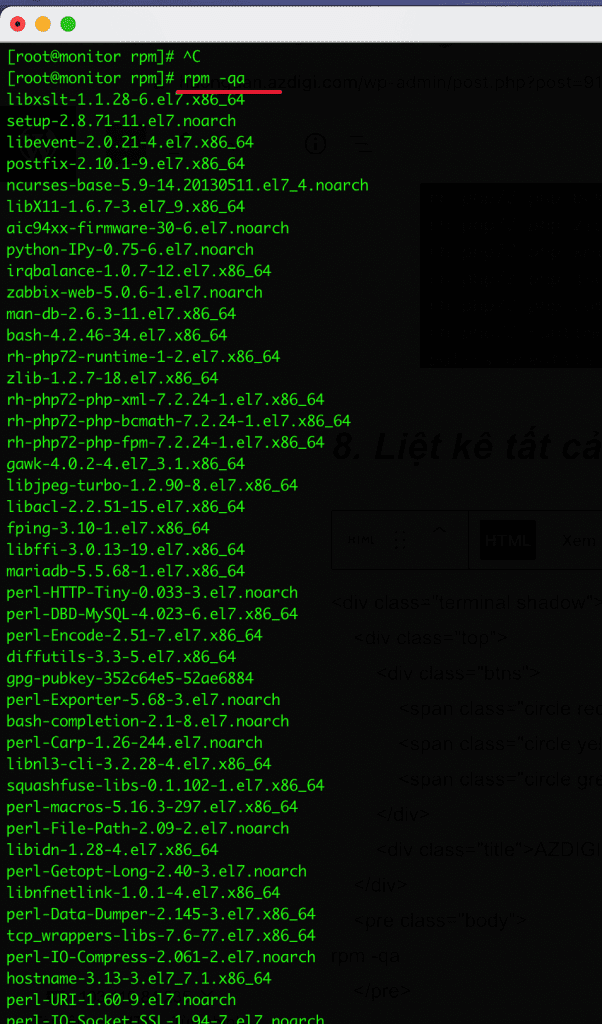
8. List all installed RPM packages
To list all installed rpm packages and Linux systems, you use the rpm command with the -qa (query all) option.
rpm -qa
9. Upgrade the RPM package
If you want to upgrade an installed rpm package, you can use the rpm command with the option -U (Upgrade) and one of the main advantages of using this option is that it will not only upgrade the new version of the package but also maintains a backup of the older package so that if the newer upgrade fails to run, it can be reused.
For example:
rpm -Uvh telnet-0.17-65.el7_8.x86_64.rpm
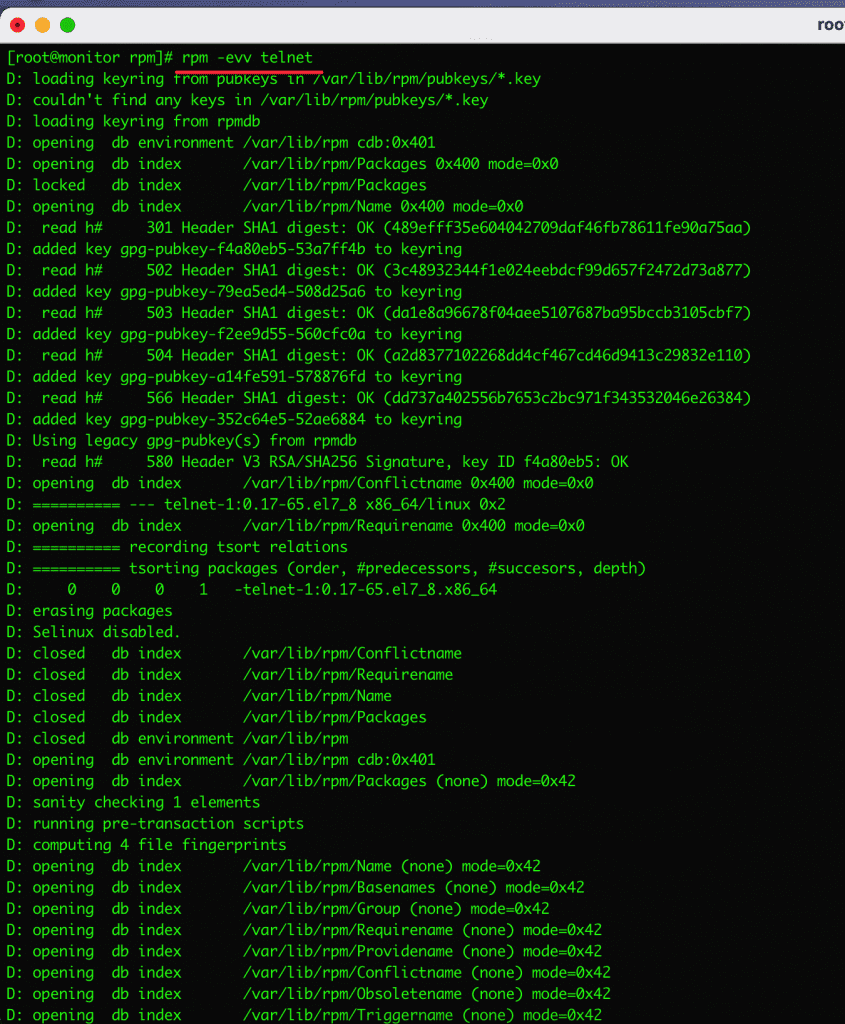
10. Remove the RPM package
To uninstall or remove the rpm package, you use the rpm command and the -e option to remove it.
Example: I will remove the telnet package.
rpm -evv telnet
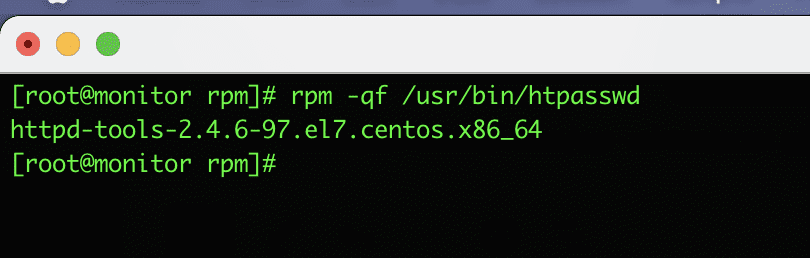
11. Query which file belongs to which RPM package on Linux
Suppose you have a list of files and you want to know which rpm package the file belongs to, you use the -qf option to check.
For example: I will check which rpm package the file /usr/bin/htpasswd belongs to with the following command:
rpm -qf /usr/bin/htpasswd
The result is a file belonging to the rpm package named httpd-tools-2.4.6-97.el7.centos.x86_64
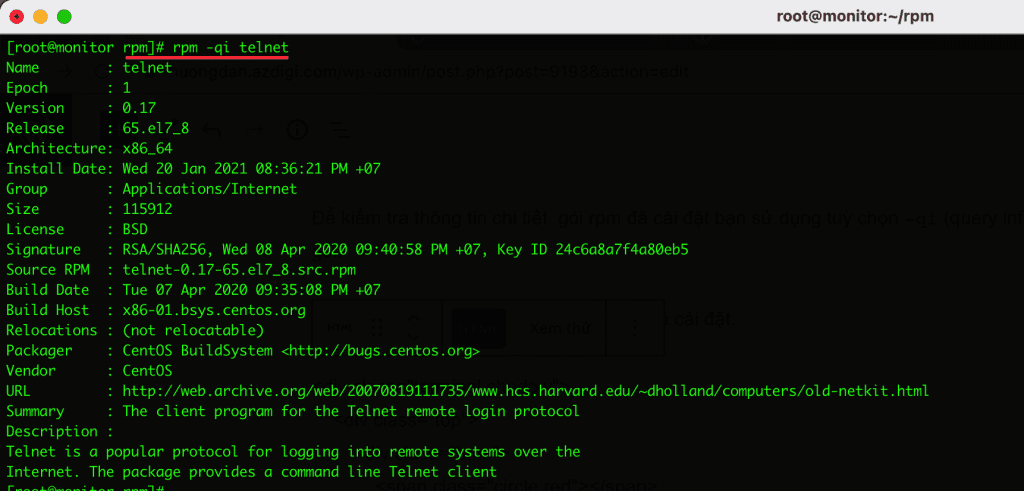
12. Query Installed RPM Package Information
To check the installed rpm package details, use the -qi (query infomation) option to view detailed package information.
Example: I will check the installed telnet package information.
rpm -qi telnet
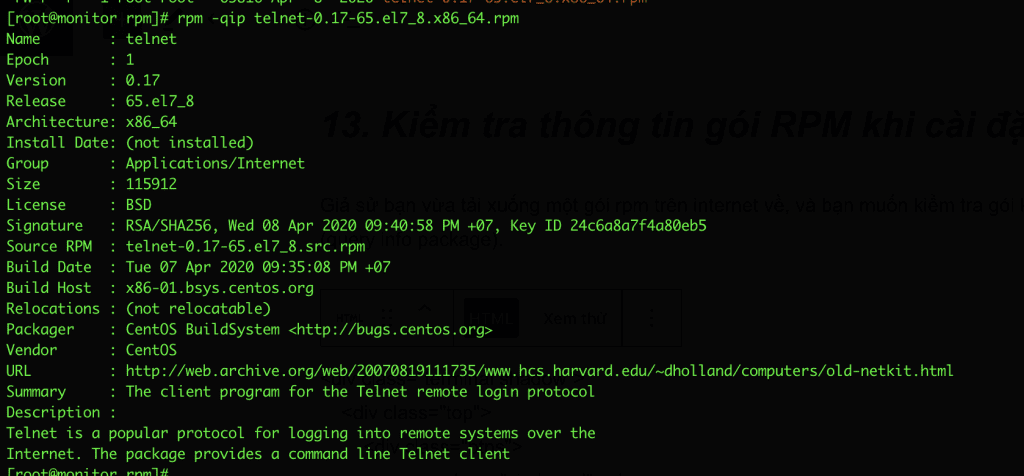
13. Check RPM package information when installing
Suppose you have just downloaded an rpm package from the internet and want to check the package when you install it, you use the -qip (query info package) option.
For example:
rpm -qip telnet-0.17-65.el7_8.x86_64.rpm
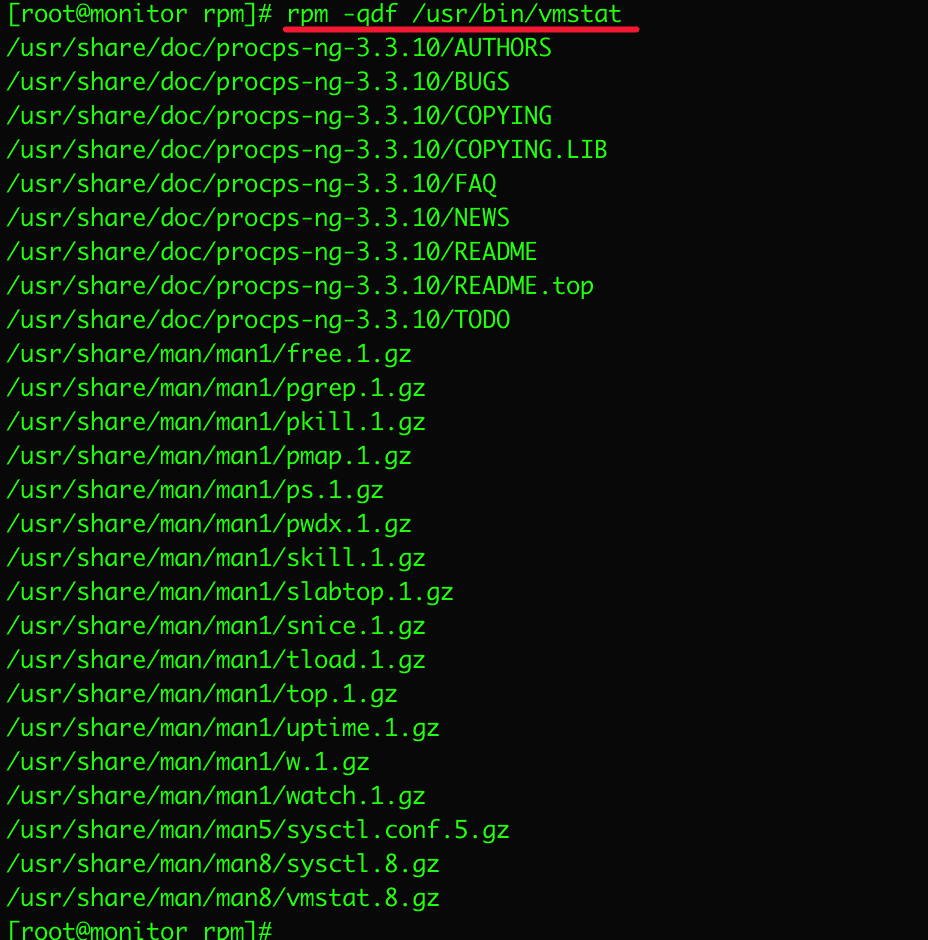
14. Query installed RPM package document
To get the list of available documents of an installed package, use the following command with the -qdf (query document file) option, it will display the pages related to the vmstat package in the example below:
rpm -qdf /usr/bin/vmstat
15. Verify RPM Package
To verify the rpm package, you use the -Vp (verify package) option.
For example, I will verify the package telnet-0.17-65.el7_8.x86_64.rpm
rpm -Vp telnet-0.17-65.el7_8.x86_64.rpm
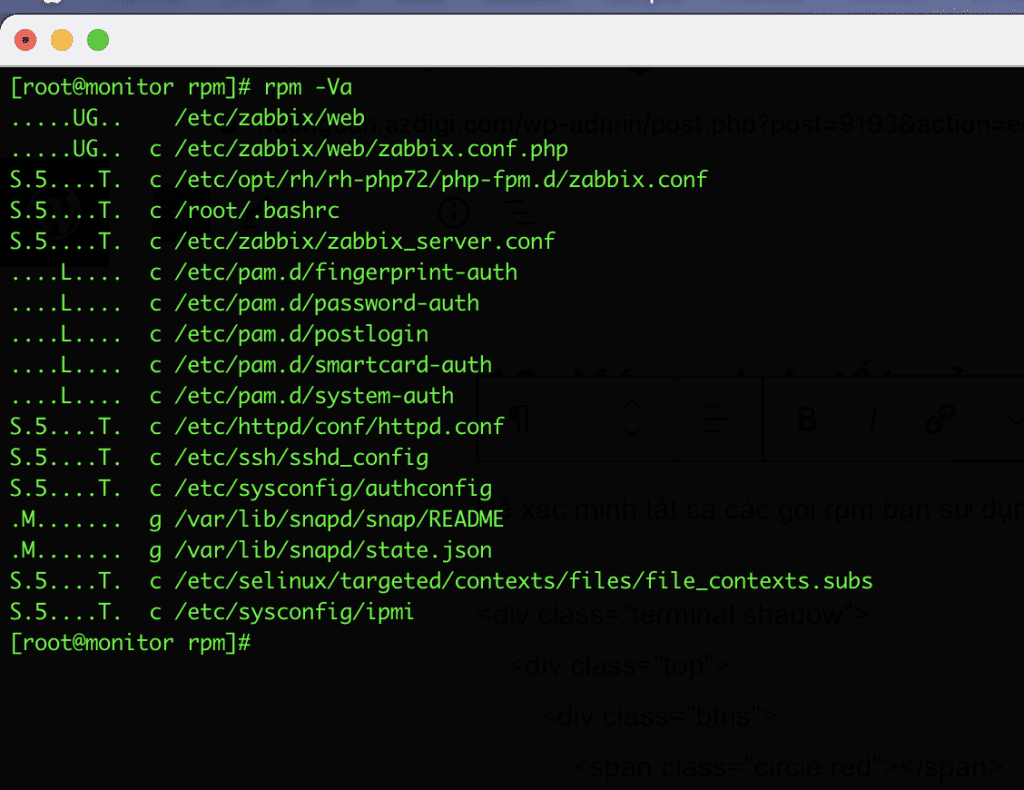
16. Verify all RPM packages
To verify all rpm packages, use the -Va (Verify all) option.
rpm -Va
17. Enter the RPM GPG key
To verify the RHEL/CentOS or Fedora package, you must enter the GPG key by using the following command: It will enter the CentOS 7 GPG key.
rpm --import /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
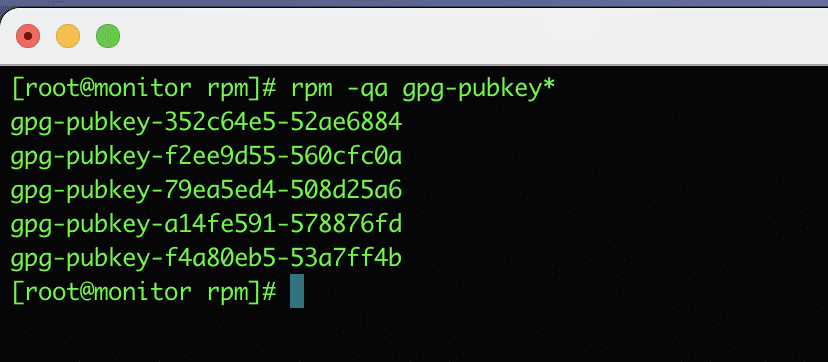
18. List all RPM GPG keys
To display all GPG keys in the system, use the following command:
rpm -qa gpg-pubkey*
19. Rebuild the corrupted RPM database
Sometimes the rpm database is corrupted, causing all rpm functions to stop and other applications on the system to. So we need to rebuild the rpm database and restore it with the following command:
cd /var/lib
rm __db*
rpm --rebuilddb
rpmdb_verify Packages
III. Summary
So AZDIGI has shown you to use basic RPM on Linux. Wishing you success! See more useful articles about Linux VPS at the following link:
If you need assistance, you can contact support in the ways below:
- Hotline 247: 028 888 24768 (Ext 0)
- Ticket/Email: You use the email to register for the service and send it directly to: support@azdigi.com .

