Nội dung
VPS (Virtual Private Server) is a form of virtual server, virtual server is created by the method of dividing a physical server into many different servers with similar features as a dedicated server, running in the form of sharing resources from the server. that original physical owner.
By default, when you register to buy a VPS at any provider, you must ensure that you have the knowledge to use, operate and manage it. Providers that sell you a VPS usually only install Control Panel for you, such as DirectAdmin free version, VestaCP, Scripts like hocvps… And you just need to use it, but you don’t understand that you need to optimize and reconfigure VPS to run better, smoother.
However, in the process of operating and using, you will have a little problem that the VPS’s capacity is full using the Linux operating system, then today’s article I will guide you how to check the capacity on Linux.
The amount of space generated during use, such as uploaded files, images, text, sources that you forgot to delete, or configure automatic backups, backup files stored in VPS for a long time will fill up.
Check capacity on Linux
Step 1: Log in to the Linux server via SSH.
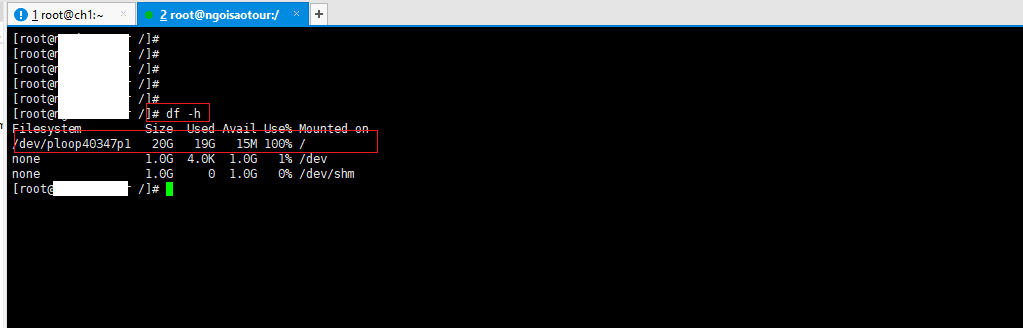
Step 2: Check the overall capacity by typing the command df -h
The message will return as follows:
[root@lab .azdigi.vn /]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/ploop40347p1 20G 19G 15M 100% / none 1.0G 4.0K 1.0G 1% /dev none 1.0G 0 1.0G 0% /dev/shm
Here you see the capacity is 100% full, only 15MB free. Apply to the partition of the root directory (also known as/ )
Check details of each folder, file
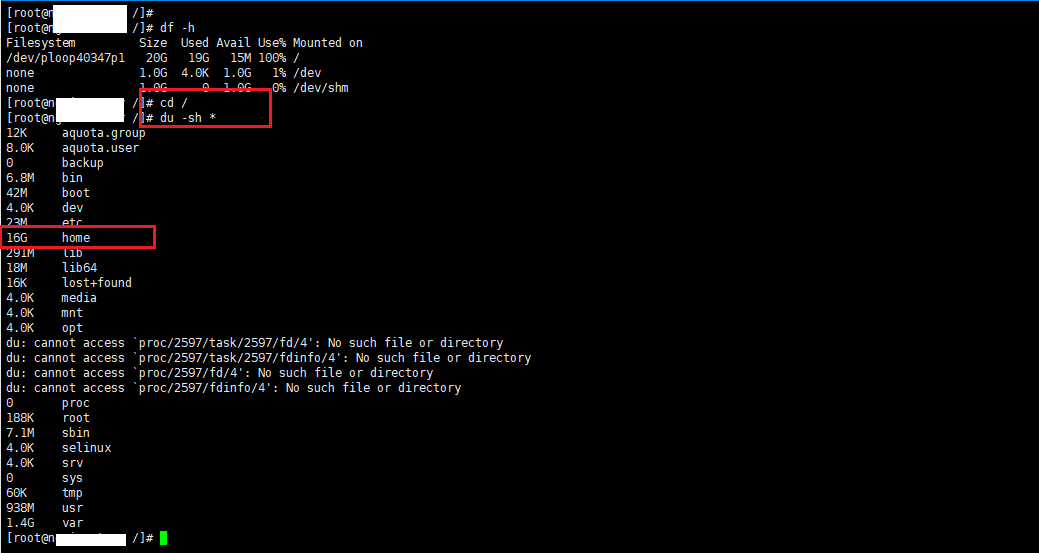
You access the root directory with the command
cd /
Next, type the command du -sh * to list the details
du -sh *
The message will return as follows
# du -sh * 12K aquota.group 8.0K aquota.user 0 backup 6.8M bin 42M boot 4.0K dev 23M etc 16G home 291M lib 18M lib64 16K lost+found 4.0K media 4.0K mnt 4.0K opt du: cannot access `proc/2597/task/2597/fd/4': No such file or directory du: cannot access `proc/2597/task/2597/fdinfo/4': No such file or directory du: cannot access `proc/2597/fd/4': No such file or directory du: cannot access `proc/2597/fdinfo/4': No such file or directory 0 proc 188K root 7.1M sbin 4.0K selinux 4.0K srv 0 sys 60K tmp 938M usr 1.4G var
At the notice on the home folder is taking up at most 16GB, continue to access the home folder
cd /home
Type in the command du -sh * to list files subdirectory in the parent directory is home
5.8G admin 11G backup
Here you will see that the admin and backup folders take up too much space. continue to access the backup folder to see what’s in it that takes up so much
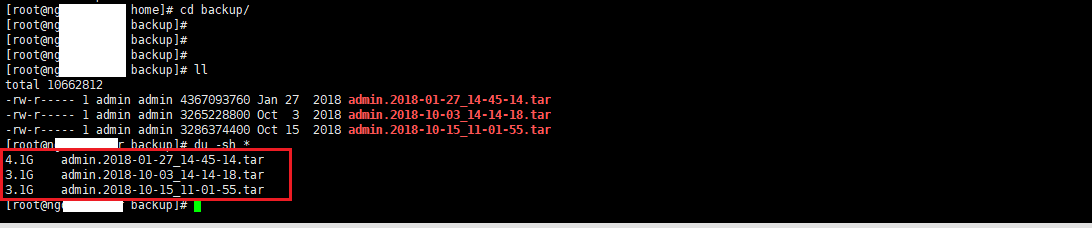
cd backup/
I typed the commandll to list, there are 3 backup files that are backed up periodically
# ll total 10662812 -rw-r----- 1 admin admin 4367093760 Jan 27 2018 admin.2018-01-27_14-45-14.tar -rw-r----- 1 admin admin 3265228800 Oct 3 2018 admin.2018-10-03_14-14-18.tar -rw-r----- 1 admin admin 3286374400 Oct 15 2018 admin.2018-10-15_11-01-55.tar
Type in the du -sh * command to list details,the return message shows that 3 files are too large, 1 file 4GB and 2 files 3GB
# du -sh * 4.1G admin.2018-01-27_14-45-14.tar 3.1G admin.2018-10-03_14-14-18.tar 3.1G admin.2018-10-15_11-01-55.tar
There are also some commands to help you find large files and folders more quickly.
Find the 5 largest files: find -type f -exec du -Sh {} + | sort -rh | head -n 5
Find the 5 largest directories: du -hs * | sort -rh | head -5
Handling files
I no longer need to use the backup files above, so I will delete them with the rm -rf command. However, you need to specify it correctly to avoid deleting it by mistake.
rm -rf admin.2018-01-27_14-45-14.tar
Wishing you success!