Introduction
As a system administrator or an individual user using the Linux operating system, you will certainly need to check the system periodically to have a solution to problems before it occurs. And one of the important things in this job is to check and list the existing disk on the server.
So why is this check important for the server? When operating, if the drives are full, the data will not be able to be written to, and if it is worse, it will lead to some services on the server not being able to work and operate or cause the service to fail (most often, it affects the webserver or Mysql services)
Surely you have heard of the importance of this problem, so how to check and list the drive on Linux? To learn through all the Disk test commands, you can refer to the article below.
Some commands to list Disk
- lsblk (list block devices)
lsblk is used to display information about storage devices. This utility is often used to determine the exact device name to be passed to the next command.
lsblk
The result will look like this:
[root@sv ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 32G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─sda2 8:2 0 31G 0 part
├─centos_sv-root 253:0 0 29G 0 lvm /
└─centos_sv-swap 253:1 0 2G 0 lvm [SWAP]
sr0 11:0 1 973M 0 rom- df -h (disk filesystem)
df -h is used to display a complete summary of the file system’s free and used hard disk space usage on Linux.
df -h
The result will look like this:
[root@sv ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 908M 0 908M 0% /dev
tmpfs 919M 8.0K 919M 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 919M 8.5M 911M 1% /run
tmpfs 919M 0 919M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos_sv-root 29G 6.4G 23G 22% /
/dev/sda1 1014M 238M 777M 24% /boot
tmpfs 184M 0 184M 0% /run/user/0- fdisk
fdisk is a utility used to manage disk partitions. Using fdisk, you can list disk partitions, create a new one, delete an existing disk partition and see the partition size.
fdisk -l
The result will look like this:
[root@sv ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 34.4 GB, 34359738368 bytes, 67108864 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x000aea60
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 2099200 67108863 32504832 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/mapper/centos_sv-root: 31.1 GB, 31130124288 bytes, 60801024 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/centos_sv-swap: 2147 MB, 2147483648 bytes, 4194304 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes- parted
parted is a useful and powerful tool to manage hard disk partitions from the command line like list, create, shrink, delete, find and rescue disk partitions. With the parted command, you can easily manage all hard disk partitions.
parted -l
The result will look like this:
[root@sv ~]# parted -l
Model: QEMU QEMU HARDDISK (scsi)
Disk /dev/sda: 34.4GB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
Partition Table: msdos
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size Type File system Flags
1 1049kB 1075MB 1074MB primary xfs boot
2 1075MB 34.4GB 33.3GB primary lvm
Model: Linux device-mapper (linear) (dm)
Disk /dev/mapper/centos_sv-swap: 2147MB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
Partition Table: loop
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size File system Flags
1 0.00B 2147MB 2147MB linux-swap(v1)
Model: Linux device-mapper (linear) (dm)
Disk /dev/mapper/centos_sv-root: 31.1GB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
Partition Table: loop
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size File system Flags
1 0.00B 31.1GB 31.1GB xfs
Warning: Unable to open /dev/sr0 read-write (Read-only file system). /dev/sr0
has been opened read-only.
Model: QEMU QEMU DVD-ROM (scsi)
Disk /dev/sr0: 1020MB
Sector size (logical/physical): 2048B/2048B
Partition Table: msdos
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size Type File system Flags
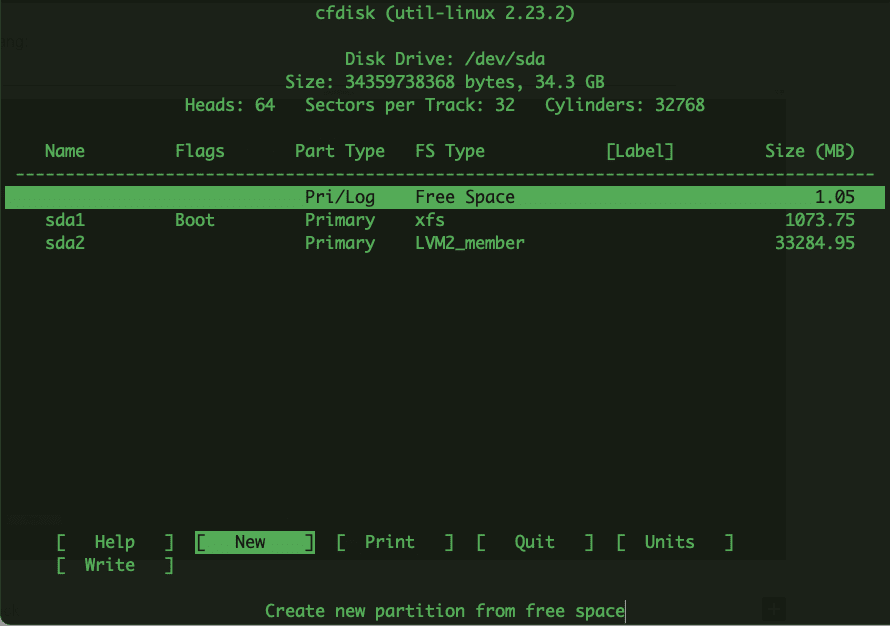
2 909kB 37.0MB 36.0MB primary- cfdisk
cfdisk will be slightly different from the commands above, it provides a graphical view in a text-based interface for disk management. Using cfdisk, you can list, create, delete, and modify partitions on a disk device.
cfdisk
The result will look like this:
- sfdisk -l
Sfdisk is a partition table editor. It can list partitions on a device, the partition size and check partitions on a device. But it isn’t designed for large partitions.
The result will look like this:
[root@sv ~]# sfdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 32768 cylinders, 64 heads, 32 sectors/track
Units: cylinders of 1048576 bytes, blocks of 1024 bytes, counting from 0
Device Boot Start End #cyls #blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 1024 1024 1048576 83 Linux
sfdisk: start: (c,h,s) expected (1,0,1) found (0,32,33)
sfdisk: end: (c,h,s) expected (1023,63,32) found (130,170,40)
/dev/sda2 1025 32767 31743 32504832 8e Linux LVM
sfdisk: start: (c,h,s) expected (1023,63,32) found (130,170,41)
sfdisk: end: (c,h,s) expected (1023,63,32) found (1023,254,63)
/dev/sda3 0 - 0 0 0 Empty
/dev/sda4 0 - 0 0 0 Empty
Disk /dev/mapper/centos_sv-root: 3784 cylinders, 255 heads, 63 sectors/track
Disk /dev/mapper/centos_sv-swap: 261 cylinders, 255 heads, 63 sectors/track- ls -l /dev/disk/by-id
The ls command is a very simple but powerful command used to list files and folders. We can list the disks using the dev/disk/by-id directory.
ls -l /dev/disk/by-id
The result will look like this:
[root@sv ~]# ls -l /dev/disk/by-id
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Apr 28 12:53 ata-QEMU_DVD-ROM_QM00003 -> ../../sr0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 May 7 23:06 dm-name-centos_sv-root -> ../../dm-0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 May 7 23:06 dm-name-centos_sv-swap -> ../../dm-1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 May 7 23:06 dm-uuid-LVM-4Tawux30vQT82EtBWqC70MdvRlurwY0OeVWa7CqfFZoOuqCm8I1jkSJBY4oYwe6m -> ../../dm-0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 May 7 23:06 dm-uuid-LVM-4Tawux30vQT82EtBWqC70MdvRlurwY0OS2E7vUg78hvYGIhr9ejMhugBXIMjvEqy -> ../../dm-1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 May 7 23:11 lvm-pv-uuid-nnRoBG-YrFq-kmzF-uhFj-cBJE-XdT1-FMkRrs -> ../../sda2
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 May 7 23:11 scsi-0QEMU_QEMU_HARDDISK_drive-scsi0 -> ../../sda
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 May 7 23:11 scsi-0QEMU_QEMU_HARDDISK_drive-scsi0-part1 -> ../../sda1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 May 7 23:11 scsi-0QEMU_QEMU_HARDDISK_drive-scsi0-part2 -> ../../sda2You can also list by:
– by-label
– by-partlabel
– by-partuuid
– by-path
– by-uuid
The above are some ways to help you check the most specific and accurate Disk partitions. This will help you monitor in detail the existing Disk partitions on the server and the internal components of that partition so that you can manipulate the most accurately.
You can refer to other instructions at the link below:
If you need assistance, you can contact support in the ways below:
- Hotline 247: 028 888 24768 (Ext 0)
- Ticket/Email: You use the email to register for the service and send it directly to: support@azdigi.com .

