Nội dung
Create a script to restart MySQL when it stops on a Linux server with 3 steps.
Introduction
In the process of using or administering a Linux server, surely you are no stranger to the Mysql service being suspended or stopped at some point for some reason. I often see Mysql being stopped when the space is full or due to excessive use of RAM resources on the server. When the RAM resources on the server are overloaded, the OOM service will have to kill the Mysql process to reduce this resource load.
If Mysql is stopped due to full capacity, you need to check and delete unnecessary data (logs,…) then you can restart Mysql. And if we fall into the case of being stopped due to overloading Ram resources or for some unknown reason, we can apply the way to create Cron like this article.
How to create a Script
Step 1: SSH into your Linux server
To make Cron start Mysql on Linux, we first need to SSH or access your VPS/server as root. If you don’t know how to SSH into your VPS/Server, you can refer to the following tutorial:
After successfully SSH, we continue with step 2 to continue the configuration.
Step 2: Create a script to check the status and start Mysql
Please follow the commands below to create the path and add the script content (you can replace the path, the file/folder name as you like).
- Create the path containing the script file
mkdir /root/auto
vi /root/auto/autostart-mysql.sh
Explanation of commands:
– Command 1: Create an auto folder at /root
– Command 2: Create file autostart-mysql.sh at /root/auto
- Add the below content to the created file
After creating the autostart-mysql.sh file, proceed to edit and paste the script content below into the file.
To determine if you are using mysqld or mariadb, you can use the command below:
netstat -nlp | grep 3306
If you are using MySQL , use the following script:
if [ ! "$(systemctl status mysql.service | awk 'NR==3 {print $2}')" == "active" ]; then
/bin/systemctl start mysql.service
exit
fi
If you are using MariaDB , use the following script:
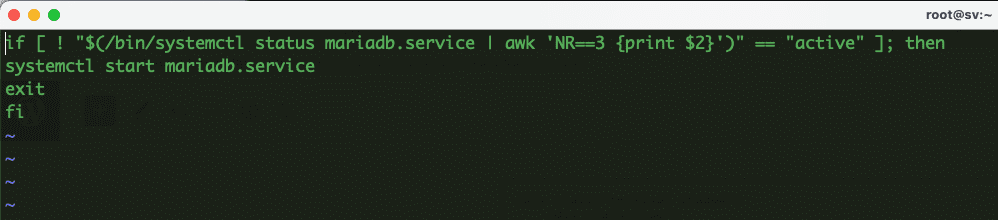
if [ ! "$(/bin/systemctl status mariadb.service | awk 'NR==3 {print $2}')" == "active" ]; then
systemctl start mariadb.service
exit
fi
Here is an example of when I add script content to the autostart-mysql.sh file. Once added, please save it.
- Permissions for the file autostart-mysql.sh
chmod +x /root/auto/autostart-mysql.sh
Step 3: Create Cron to set script runtime
Note: You should not set the Cron runtime too short (less than 5 minutes) because it will easily overload resources and cause system errors.
For example, I will set the time every 10 minutes, and the script will be run once to check the status of Mysql, if the status is stopped, it will automatically restart. Next, you set up fast Cron using the command:
(crontab -u root -l ; echo "*/10 * * * * /bin/bash /root/auto/autostart-mysql.sh") | crontab -u root -
systemctl restart crond
Explanation of the above command:
– Command 1: Set up Cron to run the script every 10 minutes and check once.
– Command 2: Restart the Crond service
So AZDIGI has shown you in detail how to create a Cron that automatically checks the status and restarts Mysql if it is stopped. This helps your website not be interrupted for too long if you cannot monitor your server 24/24. Hope this article is helpful to you, wish you success!
You can refer to other instructions at the link below:
If you need assistance, you can contact support in the ways below:
- Hotline 247: 028 888 24768 (Ext 0)
- Ticket/Email: You use the email to register for the service and send it directly to: support@azdigi.com .

