Nội dung
This article will help you with some ways to clean up the systemd journal log in order to free up the memory usage of this type of log.
I. Introduction
On any server, logs generated during usage can easily consume a lot of storage memory. Among them, the journal log takes up a relatively large and common space on Linux servers.
Usually, the journal log will be located at one of the following two paths:
/var/log/journal/
Hoặc
/run/log/journal/
And we can easily check their size with one of the following commands:
du -sh /var/log/journal/
Hoặc
du -sh /run/log/journal/
For example, if the returned result is as below, your journal log takes up 4.1GB:
du -hs /var/log/journal/
4.1G /var/log/journal/
Usually, we don’t really need that many logs, so let’s clean them up with some of the methods below.
II. Cleaning up the systemd journal log
To clean up the systemd journal log, we need to SSH into our server first. Or at least log in to the server with a user with sudo privileges. If you don’t know how to SSH into your VPS/Server, you can refer to the following tutorial:
After successfully SSH, we can refer to some ways to clean up the systemd journal log as follows:
Method 1: Delete systemd journal logs older than X days
In this first method, I will help you delete systemd journal logs older than 10 days. And this is also the most commonly used method.
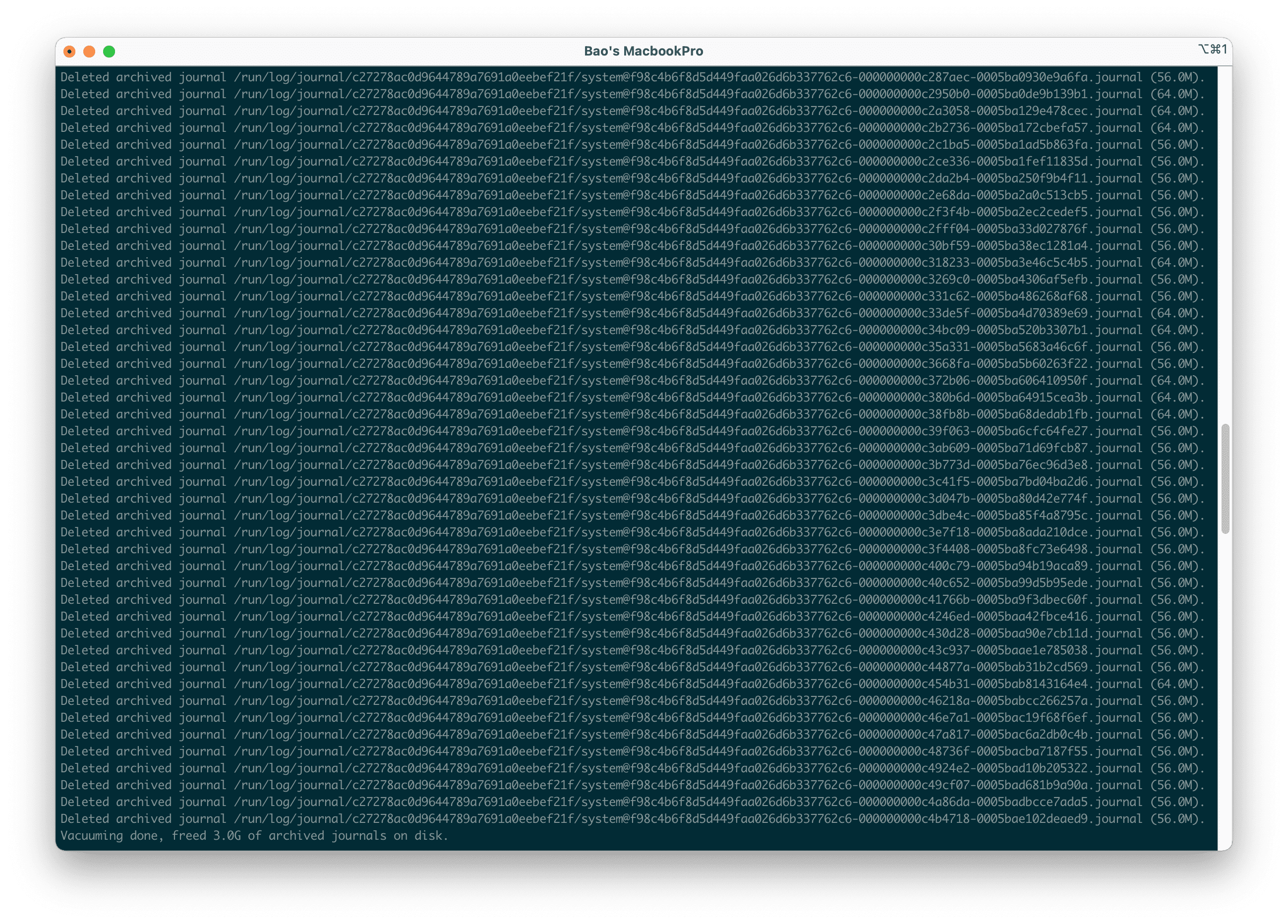
journalctl --vacuum-time=10d
Here is my result after running the command: Depending on each system, the amount of storage cleared will vary.
Method 2: Clean up the systemd journal log if it exceeds X
With this method, we can choose to delete the systemd journal log if its size exceeds XGB, XMB, and so on.
If you want to keep only 20MB of logs, you can use the following command:
journalctl --vacuum-size=20M
Or if you want to keep 1GB, you can use the following command:
journalctl --vacuum-size=1G
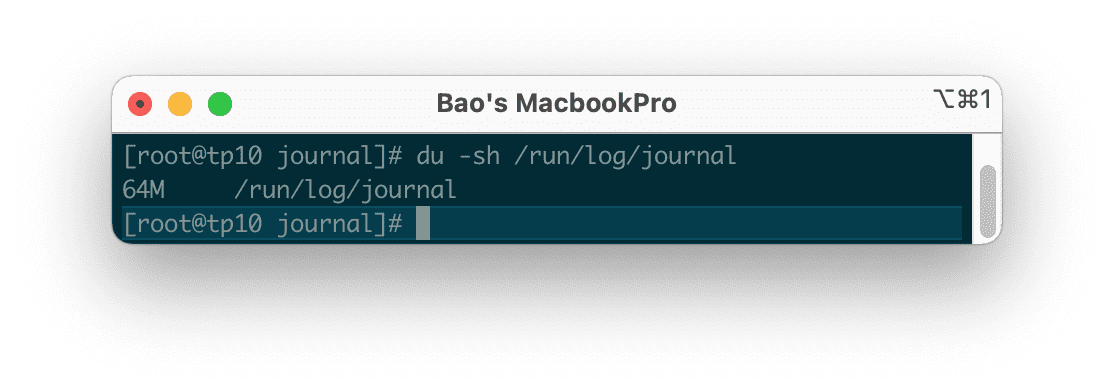
After cleaning up, you can check the remaining journal log size on the system with either of the following commands:
du -sh /var/log/journal/
Hoặc
du -sh /run/log/journal/
And you can also configure one of the log deletion commands in Crontab. From then on, your system will automatically clean up according to the schedule set.
III. Summary
Hopefully, these two methods of cleaning up the systemd journal log from AZDIGI will help you free up a lot of storage space on your system. Besides the systemd journal log, there are many other logs, but in this article, I only mentioned the systemd journal log. Because different Linux systems will use different services, the logs will also vary.

